Language
LanguageDefinition of lead-acid battery industry
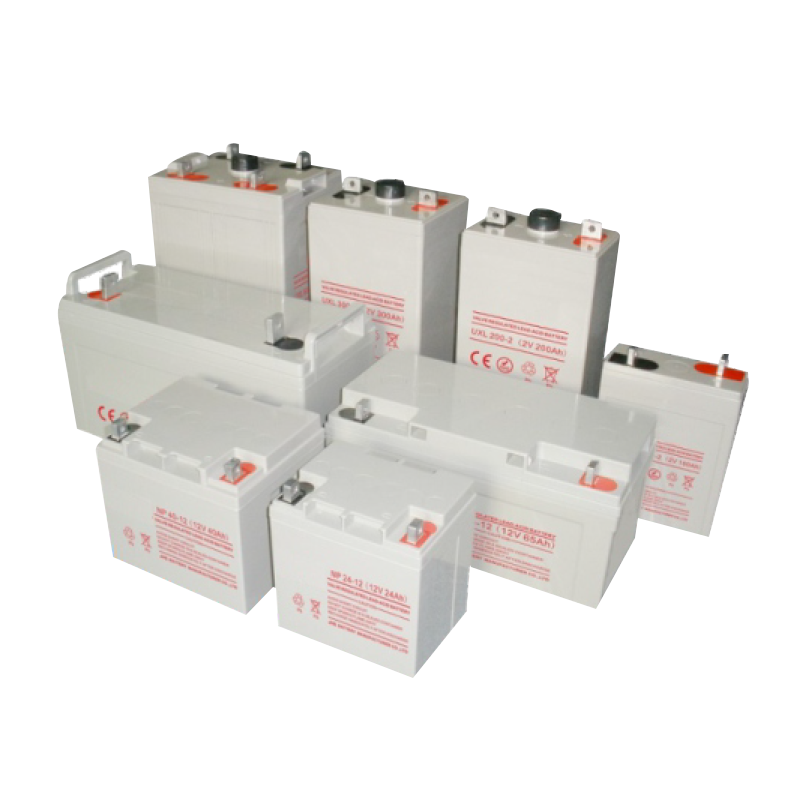
In addition to lithium batteries, lead-acid batteries are also a very important battery system in commonly used rechargeable batteries. The advantage of lead-acid batteries is that their electromotive force is relatively stable during discharge, but the disadvantage is that their specific energy (stored energy per unit weight) is small and they are highly corrosive to the environment. Lead acid batteries have a stable working voltage, a wide range of operating temperatures and currents, the ability to charge and discharge hundreds of cycles, good storage performance (especially suitable for dry charge storage), and low cost, making them widely used.
Lead acid battery: Its volume and weight have not been effectively improved, so it is currently most commonly used in car and motorcycle engines. The biggest improvement of lead-acid batteries is the recent use of high-efficiency oxygen recombination technology to complete water regeneration, achieving the goal of complete sealing without the need for water. The "water free battery" made from it can have a lifespan of up to 4 years (single electrode voltage 2V).
Lead acid batteries have a history of over 150 years since their invention by Plant in 1859, and their technology is very mature, making them the most widely used chemical power source in the world. Despite the emergence and application of new types of batteries such as nickel cadmium batteries, nickel hydrogen batteries, and lithium-ion batteries in recent years, lead-acid batteries still hold a solid position in the vast majority of traditional and emerging application fields due to their strong high current discharge performance, stable voltage characteristics, wide temperature applicability, large single cell capacity, high safety, abundant and renewable raw materials, and low prices.
Classification of lead-acid batteries
(1) According to the structure of battery plates, there are formation type, paste type, and tube type batteries;
(2) Classified by battery cover and structure: there are open type, exhaust type, acid proof and explosion-proof type, and sealed valve controlled type batteries;
(3) Classified by battery maintenance methods: there are regular, low maintenance, and maintenance free batteries.
(4) According to relevant national standards, the main battery series products include:
Starting type batteries: mainly used for starting and lighting in automobiles, tractors, diesel powered ships, etc;
Fixed battery: mainly used as a backup power source for protection and automatic control in communication, power plants, and computer systems;
Traction type batteries: mainly used for various power sources such as battery trucks, * * * * trucks, and forklifts;
Railway batteries: mainly used for starting and lighting power of railway internal combustion locomotives, electric locomotives, and passenger cars;
Motorcycle batteries: mainly used for starting and lighting various specifications of motorcycles;
Coal mine batteries: mainly used for traction power supply of electric locomotives;
Energy storage batteries: mainly used for wind and hydropower energy storage.